多流转换算子
许多应用需要摄入多个流并将流合并处理,还可能需要将一条流分割成多条流然后针对每一条流应用不同的业务逻辑。接下来,我们将讨论DataStream API中提供的能够处理多条输入流或者发送多条输出流的操作算子。
UNION
DataStream.union()方法将两条或者多条DataStream合并成一条具有与输入流相同类型的输出DataStream。接下来的转换算子将会处理输入流中的所有元素。图5-5展示了union操作符如何将黑色和白色的事件流合并成一个单一输出流。
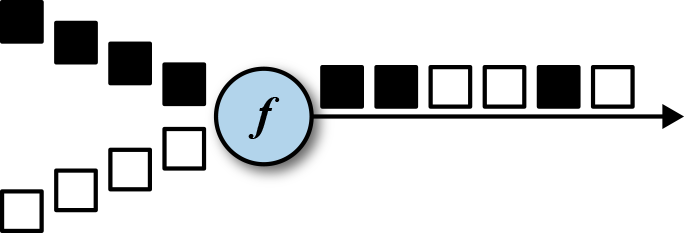
事件合流的方式为FIFO方式。操作符并不会产生一个特定顺序的事件流。union操作符也不会进行去重。每一个输入事件都被发送到了下一个操作符。
下面的例子展示了如何将三条类型为SensorReading的数据流合并成一条流。
scala version
val parisStream: DataStream[SensorReading] = ...
val tokyoStream: DataStream[SensorReading] = ...
val rioStream: DataStream[SensorReading] = ...
val allCities: DataStream[SensorReading] = parisStream
.union(tokyoStream, rioStream)
java version
DataStream<SensorReading> parisStream = ...
DataStream<SensorReading> tokyoStream = ...
DataStream<SensorReading> rioStream = ...
DataStream<SensorReading> allCities = parisStream
.union(tokyoStream, rioStream)
CONNECT, COMAP和COFLATMAP
联合两条流的事件是非常常见的流处理需求。例如监控一片森林然后发出高危的火警警报。报警的Application接收两条流,一条是温度传感器传回来的数据,一条是烟雾传感器传回来的数据。当两条流都超过各自的阈值时,报警。
DataStream API提供了connect操作来支持以上的应用场景。DataStream.connect()方法接收一条DataStream,然后返回一个ConnectedStreams类型的对象,这个对象表示了两条连接的流。
scala version
val first = ...
val second = ...
val connected = first.connect(second)
java version
// first stream
DataStream<Integer> first = ...
// second stream
DataStream<String> second = ...
// connect streams
ConnectedStreams<Integer, String> connected = first.connect(second);
ConnectedStreams提供了map()和flatMap()方法,分别需要接收类型为CoMapFunction和CoFlatMapFunction的参数。
以上两个函数里面的泛型是第一条流的事件类型和第二条流的事件类型,以及输出流的事件类型。还定义了两个方法,每一个方法针对一条流来调用。map1()和flatMap1()会调用在第一条流的元素上面,map2()和flatMap2()会调用在第二条流的元素上面。
// IN1: 第一条流的事件类型
// IN2: 第二条流的事件类型
// OUT: 输出流的事件类型
CoMapFunction[IN1, IN2, OUT]
> map1(IN1): OUT
> map2(IN2): OUT
CoFlatMapFunction[IN1, IN2, OUT]
> flatMap1(IN1, Collector[OUT]): Unit
> flatMap2(IN2, Collector[OUT]): Unit
函数无法选择读某一条流。我们是无法控制函数中的两个方法的调用顺序的。当一条流中的元素到来时,将会调用相对应的方法。
对两条流做连接查询通常需要这两条流基于某些条件被确定性的路由到操作符中相同的并行实例里面去。在默认情况下,connect()操作将不会对两条流的事件建立任何关系,所以两条流的事件将会随机的被发送到下游的算子实例里面去。这样的行为会产生不确定性的计算结果,显然不是我们想要的。为了针对ConnectedStreams进行确定性的转换操作,connect()方法可以和keyBy()或者broadcast()组合起来使用。我们首先看一下keyBy()的示例。
scala version
val one = ...
val two = ...
val keyedConnect1 = one.connect(two).keyBy(0, 0)
val keyedConnect2 = one.keyBy(0).connect(two.keyBy(0))
java version
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, Long>> one = ...
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, String>> two = ...
// keyBy two connected streams
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<Int, Long>, Tuple2<Integer, String>> keyedConnect1 = one
.connect(two)
.keyBy(0, 0); // key both input streams on first attribute
// alternative: connect two keyed streams
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<Integer, Long>, Tuple2<Integer, String>> keyedConnect2 = one
.keyBy(0)
.connect(two.keyBy(0));
无论使用keyBy()算子操作ConnectedStreams还是使用connect()算子连接两条KeyedStreams,connect()算子会将两条流的含有相同Key的所有事件都发送到相同的算子实例。两条流的key必须是一样的类型和值,就像SQL中的JOIN。在connected和keyed stream上面执行的算子有访问keyed state的权限。
下面的例子展示了如何连接一条DataStream和广播过的流。
scala version
val one = ...
val two = ...
val keyedConnect = first.connect(second.broadcast())
java version
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, Long>> one = ...
DataStream<Tuple2<Int, String>> two = ...
// connect streams with broadcast
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<Int, Long>, Tuple2<Int, String>> keyedConnect = first
// broadcast second input stream
.connect(second.broadcast());
一条被广播过的流中的所有元素将会被复制然后发送到下游算子的所有并行实例中去。未被广播过的流仅仅向前发送。所以两条流的元素显然会被连接处理。
例子:
警告类:
scala version
case class Alert(message: String, timestamp: Long)
java version
public class Alert {
public String message;
public long timestamp;
public Alert() { }
public Alert(String message, long timestamp) {
this.message = message;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + message + ", " + timestamp + ")";
}
}
烟雾传感器读数类:
public enum SmokeLevel {
LOW,
HIGH
}
产生烟雾传感器读数的自定义数据源:
public class SmokeLevelSource implements SourceFunction<SmokeLevel> {
private boolean running = true;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<SmokeLevel> srcCtx) throws Exception {
Random rand = new Random();
while (running) {
if (rand.nextGaussian() > 0.8) {
srcCtx.collect(SmokeLevel.HIGH);
} else {
srcCtx.collect(SmokeLevel.LOW);
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
this.running = false;
}
}
监控一片森林然后发出高危的火警警报。报警的Application接收两条流,一条是温度传感器传回来的数据,一条是烟雾传感器传回来的数据。当两条流都超过各自的阈值时,报警。
scala version
object MultiStreamTransformations {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val tempReadings = env.addSource(new SensorSource)
val smokeReadings = env
.addSource(new SmokeLevelSource)
.setParallelism(1)
val keyedTempReadings = tempReadings
.keyBy(r => r.id)
val alerts = keyedTempReadings
.connect(smokeReadings.broadcast())
.flatMap(new RaiseAlertFlatMap)
alerts.print()
env.execute("Multi-Stream Transformations Example")
}
class RaiseAlertFlatMap extends CoFlatMapFunction[SensorReading, SmokeLevel, Alert] {
private var smokeLevel = "LOW"
override def flatMap1(tempReading: SensorReading, out: Collector[Alert]) : Unit = {
if (smokeLevel == "HIGH" && tempReading.temperature > 100) {
out.collect(Alert("Risk of fire! " + tempReading, tempReading.timestamp))
}
}
override def flatMap2(sl: String, out: Collector[Alert]) : Unit = {
smokeLevel = sl
}
}
}
java version
public class MultiStreamTransformations {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<SensorReading> tempReadings = env
.addSource(new SensorSource());
DataStream<SmokeLevel> smokeReadings = env
.addSource(new SmokeLevelSource())
.setParallelism(1);
KeyedStream<SensorReading, String> keyedTempReadings = tempReadings
.keyBy(r -> r.id);
DataStream<Alert> alerts = keyedTempReadings
.connect(smokeReadings.broadcast())
.flatMap(new RaiseAlertFlatMap());
alerts.print();
env.execute("Multi-Stream Transformations Example");
}
public static class RaiseAlertFlatMap implements CoFlatMapFunction<SensorReading, SmokeLevel, Alert> {
private SmokeLevel smokeLevel = SmokeLevel.LOW;
@Override
public void flatMap1(SensorReading tempReading, Collector<Alert> out) throws Exception {
// high chance of fire => true
if (this.smokeLevel == SmokeLevel.HIGH && tempReading.temperature > 100) {
out.collect(new Alert("Risk of fire! " + tempReading, tempReading.timestamp));
}
}
@Override
public void flatMap2(SmokeLevel smokeLevel, Collector<Alert> out) {
// update smoke level
this.smokeLevel = smokeLevel;
}
}
}